In today’s rapidly evolving global market, businesses face the challenge of catering to a diverse audience with varying needs and preferences. Here is where the concept of “Glocalization” is useful — a dynamic strategy that combines the best of global and local attributes to create a customized and responsive product. Traditionally, when businesses faced the challenge of adapting their offerings to various regions or markets, they would resort to decoupling their global entities. In this approach, the entire product or service is extensively customized on a regional level, resulting in complete localization and detached from the global context. A more refined approach to this decoupling is achieved by isolating only those attributes that require local variations. This means the global product or service remains universally applicable and is inherited by underlying regions and/or countries. Only the essential attributes are decoupled and localized. In essence, it represents a fusion of global and local elements, a concept commonly referred to as “Glocalization.”
The term entered use in the English-speaking world via Ronald Robertson in the 1990s and became popular in business and culture. According to Roland Robertson, glocalization signifies the simultaneous existence of both universalizing and particularizing tendencies.
In this article, we explore how SunTec is revolutionizing Glocalization through our platform SunTec Xelerate by enabling businesses to excel without decoupling their global entities.
SunTec Xelerate: A Game-changer in Glocalization
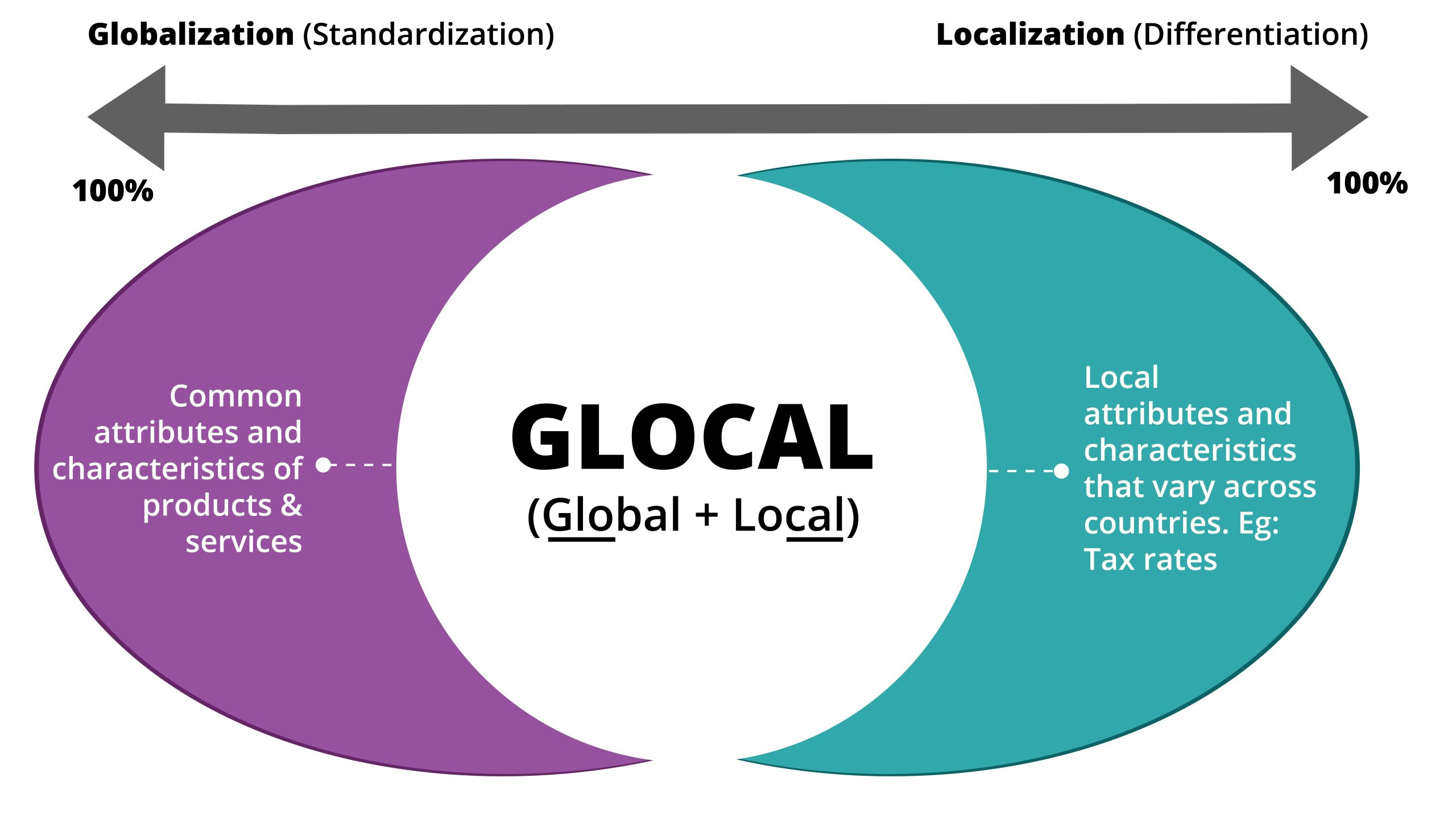
Glocalization is a combination of “globalization” and “localization.” It is a strategic approach that seeks to balance the standardization of global products or services with the localizations required to meet local demands. This approach acknowledges that while certain features and functionalities can be standardized globally, others must be tailored to specific regions or markets.
One of the key challenges in implementing localization is dealing with attributes that vary at the regional and/or local level. Historically, addressing such disparities often required the decoupling or localization of global entities, resulting in complex and resource-intensive processes. Every localized record represents an additional instance of the global record, necessitating separate maintenance for each local copy. This cumulative maintenance effort compounds as more local records are created.
Decoupling global entities had several drawbacks. It was time-consuming, resource-intensive, and often led to inefficiencies. It also dilutes the consistency and brand identity of the global product. SunTec Xelerate empowers businesses to embrace regional variations without sacrificing the integrity of their global offerings. How does SunTec Xelerate achieve this? The process of implementing glocalization can be described as follows:
Global products and services are centralized at the highest level to avoid duplication across multiple countries. These globally accessible offerings are subsequently utilized across various countries at lower tiers. The products and services passed down from higher to lower levels are designated as ‘Inherited records’. When a specific country wishes to introduce variations tailored to local needs, this configuration can occur either at the record level or the attribute level.
Record level refers to entire data or complete set of attributes of an entity. In record level deviation, the entire data or in other words the complete set of attributes of the product or service entity deviates. Attribute level refers to individual piece of information or characteristics within an entity. In attribute-level deviation, only the required attribute, which in other words is the individual piece of information of this product or service entity, deviates. The focus is on offering a balance between global consistency and local variants in the customer experience.
When record-level deviation happens, the entire entity or record becomes self-contained. This is referred to as ‘Localization’. This local version can still tie back to the global primary. Alternatively, when a localized deviation has occurred, the local version takes preference over the global contextual link. However, each localized record constitutes an additional manifestation, requiring distinct upkeep for every local record. This maintenance effort escalates with the proliferation of local records.
As described above, when attribute level deviation occurs, the entire dataset does not function in absolute isolation. Only the necessary attributes stand independently, tailored to meet local requirements, while maintaining a connection to the global bank’s services and brand standards. This process is known as ‘Glocalization.’
SunTec Xelerate provides an option to reverse a glocalization process, in which the attribute reverts to its original global value currently in effect. At any point, SunTec Xelerate offers users an ability to track the historical changes that have occurred.
By offering a comprehensive solution for handling regional attributes, SunTec Xelerate enhances compliance and efficiency. Businesses can adapt to changing regulatory requirements, tax codes, and market preferences with ease, ensuring that their products or services remain competitive and compliant in every region and/or country.
Varied tax rules and regulations exist across different countries. Banks can optimize their operations, forge deeper customer relationships, and accommodate evolving regulatory requirements, including differing tax rates. When tax rates differ regionally or locally, banks can tailor the tax element independently while maintaining a consistent global product and service framework. This serves as a prime example of glocalization that can be accomplished using SunTec Xelerate.
Why is Glocalization Important?
When a company expands into a new market, it is important to ‘glocalize’ its products and services to be successful. This involves modifying their global product to align with local market requirements, adhering to local regulations, and catering to customer preferences. For example, an American automotive company that wants to enter the Indian market would need to produce right-hand drive cars, that is the norm in the country.

Glocalization is important because it helps companies to:
- Amplify Sales and Expand Market Presence: Glocalization encourages companies to offer products and services that are tailored to the local market. Businesses can capture a broader consumer base, ultimately boosting their sales and market share.
- Foster Stronger Customer Relations: A company’s success is closely linked to its ability to understand and cater to the specific needs and preferences of its customers. When customers perceive a company’s dedication to fine tuning, it inevitably results in increased customer loyalty and the development of long-lasting relationships.
- Mitigate Cultural Pitfalls: When serving a diverse market companies may not be aware of the cultural nuances and are prone to make mistakes unintentionally. This could offend the local customers. Glocalization serves as a safeguard for businesses operating across diverse international markets.
- Provide Consistency for Multinational Customers: Multinational customers benefit from the consistent quality and offerings across their global footprint, enhancing their trust and reliance on the company. This also grants the company a significant competitive advantage in the global market.
Here are some examples of glocalization across various industries:
- McDonald’s is a global fast-food chain that has effectively adapted its menu to suit various local markets through the process of glocalization. For example, in India, McDonald’s offers a variety of vegetarian and vegan options to cater to the large vegetarian population. In Japan, McDonald’s offers a variety of seafood dishes, which are popular in Japanese cuisine. McDonald’s glocalization strategy, as seen in India and Japan, illustrates the art of blending global brand consistency with local culinary adaptation. This approach is not only about meeting local tastes but also about understanding and respecting local food cultures, which enhances customer satisfaction.
- Google Pixel glocalized its phones to comply with Indian regulations. Pixel phones initially allowed users to turn off the shutter sound. In response to Indian regulations, which mandate an audible shutter sound for camera phones, Google modified Pixel phones to ensure that they produce a shutter sound in India to adhere to local regulations.
- In the context of banking, a global bank’s advertising campaign was prominently displayed in airports across the globe. Their tagline skillfully encapsulated the bank’s dual identity, balancing its global and local aspects. What distinguishes this institution is its focus on to modifying products and services to suit the distinctive needs of each local market. A prime example was their premier product, which empowers customers to open accounts in 37 countries, ensuring support that is accessible no matter where they are. This unique strategy enabled the bank to establish itself as an institution with a vast global presence while remaining exceptionally flexible and committed to meeting the specific preferences of its local customer base. In other words, the bank’s distinct approach helps to position them as an institution with an extensive global footprint, yet one that remains highly adaptable, dedicated to fulfilling the distinctive preferences of local clientele. This insightful glocalization strategy provides an invaluable lesson for other global brands to consider. In today’s global banking landscape, glocalization is a critical growth strategy. However, the ability to unlock true glocalization, is enabled through tailoring the standard product set and service offerings to precisely match the unique demands of global, regional, or even local markets. This enables the banks to strengthen sales, build long-lasting customer relationships, and confidently navigate cultural differences.
The Future of Glocalization with SunTec Xelerate
The global business landscape is continuously evolving. Companies are seeking to expand their market presence aiming to broaden their reach across this global market to meet diverse customer needs. Given the dynamic global business environment, complexities associated with global, regional, and local market dynamics must be acknowledged and addressed when serving customer needs. The significance of glocalization becomes increasingly prominent for businesses that aspire to expand their global footprint and cater to a diverse customer base. SunTec Xelerate not only tackles the challenges associated with global, regional, and local characteristics but also fosters unparalleled innovation and growth.
Glocalization’s strength lies in its ability to uphold a delicate balance between global consistency, regional coherence, and local necessity. SunTec Xelerate embodies this balance by granting businesses the authority to adapt, monitor, and manage specific attributes while preserving the integrity of their global or regional offerings. As companies embrace this dynamic approach, they position themselves for triumph in an ever-changing world.
Integrating the intricacies of glocalization into your business strategy is no longer optional; it’s an essential necessity. With SunTec Xelerate, organizations gain access to the expertise and tools required for effortlessly navigating the intricacies of global, regional, and local attributes. Now is the time to embrace the future of glocalization to unlock new opportunities for your enterprise, and we are here to assist with our deep cross-industry knowledge and market leading SunTec Xelerate platform.