The emergence of technology has revolutionized the financial industry by transforming customer expectations and the way certain banking functions and practices are conducted. Merchant billing is one such example. This segment is experiencing significant changes due to the rise of digital and mobile payments. To remain competitive merchant banking businesses must invest in technology that modernizes, automates, consolidates, and simplifies their revenue management, billing, and payment processing functions.
What is Merchant Billing?
Merchant billing refers to the process of signing up with a merchant payment provider to invoice and collect payment (credit cards, debit cards, QR code, and other forms of payment) for goods or services rendered by a merchant using a Point of Sale (POS) system. When a customer makes a purchase at a physical store or through an online platform, the merchant uses the POS system to generate a bill or invoice for the transaction. This is a crucial service because it enables merchants to expand their payment options beyond cash and checks, making it easier and more convenient for customers to pay for goods and services. Merchant billing involves multiple stakeholders ranging from merchants and payment processors to banks and card networks, and each one plays a critical role in ensuring seamless and secure payments. Merchant services sit at the heart of the payment process that connects a business and its customers by enabling seamless and secure transfer of money.
Typically, when a payment transaction is initiated by the merchant in a PoS terminal the machine connects to the acquirer bank and asks for customer authentication. As a next step the card issuer or bank is contacted for approval via payment networks, and the bank performs some checks to ensure validity of the transaction before approving it. This is communicated back to the POS terminal and a receipt is generated.
The Merchant PoS Lifecycle and Revenue Models
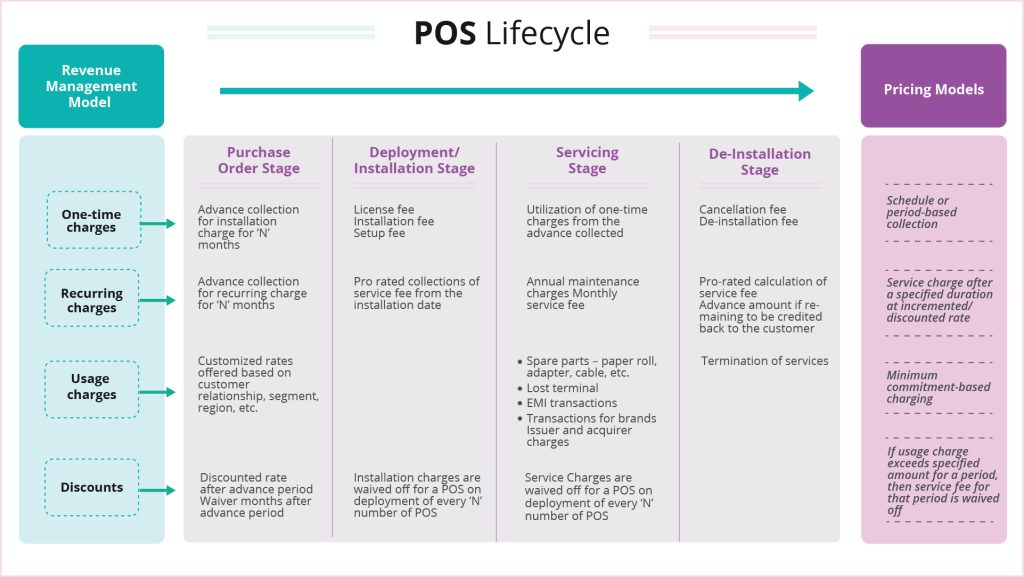
To avail of merchant services, merchants typically engage with service providers such as financial institutions or new gen fintechs with payment licenses. An engagement between the merchant and the service provider involves a set of specific steps that cover the lifecycle – from setting up the PoS terminal at start of the engagement, to the day-to-day functioning and even the end of the contract. A company picks their payment and revenue model based on these steps in the lifecycle. The entire merchant billing lifecycle includes the following stages:
-
- Installation Stage: This is the first stage in the merchant billing lifecycle where the merchant and the service provider reach an agreement on the details of the engagement. This includes factors like number of POS machines to be installed, value-added services (VAS) to be added, linking of commercial plans, price negotiations, and an optional advance payment. The revenue model adhered to at this stage usually involves one-time advance payment for the installation to be kicked off. Any customized pricing agreed to by the parties reflect in the advance payment at this stage.
-
- Deployment Stage: Once the agreement is finalized and approved, this is the second stage where the POS and VAS are deployed in the respective stores of the merchant. This marks the beginning of the engagement and entails a license fee, an installation charge or a setup fee. This is usually a one-time cost.
-
- Servicing Stage: This is the duration of the engagement that includes maintenance of the PoS equipment and other related fixtures. This stage involves usage charges or charges on the transactions taking place on the POS machine as per the terms of the agreement. There can also be a maintenance or service fee at this stage. It also includes event-based charges for office supplies, computer hardware, lost terminals, spare parts like adapter, cable, etc. collected as and when the event occurs.
-
- De-installation Stage: This is the final stage in the lifecycle where both parties decide to end the engagement. This requires a de-installation of the PoS equipment and a de-installation charge to be paid before the POS can be removed and engagement terminated. If there is any unutilized money from the advance payment at the time of contract termination, it is credited to the merchant at this point or adjusted against de-installation charges.
In addition to these lifecycle stages, a merchant banking engagement can also include:
- Discounts : Discounts are a tried and tested strategy for ensuring customer and partner satisfaction and loyalty. In this, a discounted rate is applied after the advance period. For example, installation charges for POS devices can be waived after a fixed number of POS devices are installed. If the usage charge exceeds a certain threshold, then service fees for that period can be waived off. In fact, there are multiple kinds of discount models. Another model provides a discounted charge post the advance period if the merchant opts in for advance payment for a specific period.
Of course, one size does not fit all when it comes to banking, and this is true for merchant billing as well. Different organizations have different requirements and accordingly, there must be multiple revenue management models across the entire billing lifecycle. A robust revenue management platform can manage revenue management multiple models seamlessly and efficiently.
How SunTec Xelerate Can Help with Merchant Billing
Merchant billing is a critical service that enables businesses to expand their payment options. A merchant billing engagement is a complex lifecycle with multiple steps and multiple payment and pricing options. Without a robust revenue management platform, organizations may find it challenging to manage this lifecycle efficiently, leading to errors and revenue leakage.
SunTec Xelerate is a powerful cloud-based revenue management platform that plays a key role in merchant billing digital transformation. The modules on the SunTec Xelerate platform can help automate the end-to-end revenue management process starting from merchant onboarding and product catalog setup, relationship pricing, to invoicing, and payment processing. It can provide insights on optimizing billing processes, improving pricing and accounting, and ultimately helping increase revenues. SunTec Xelerate platform’s robust pricing functionalities allow optimization of revenue by dynamically adjusting pricing based on various factors such as demand, competition, and customer behavior.
The centralized revenue management and billing platform provides real-time reporting and analytics, which helps merchants gain insights into their revenue streams. This helps merchants to make informed pricing decisions that can improve profitability, manage inventory, and stay competitive. It also helps analyze large volumes of data, making pricing recommendations based on historical trends, and current market conditions. End-to-end payment management helps merchants recover the invoiced amounts from customers via proactive and reactive modes of payments. The collection management further supports in invoice follow up, dunning actions, and penalty computation. A comprehensive pricing engine is a valuable tool for companies looking to optimize their pricing strategy and increase revenue.